Blog
2 – Code Syntax (CSS Syntax) – Selectors Properties & Values Level 1
🟦 Level 1: CSS Basics
3. CSS Syntax
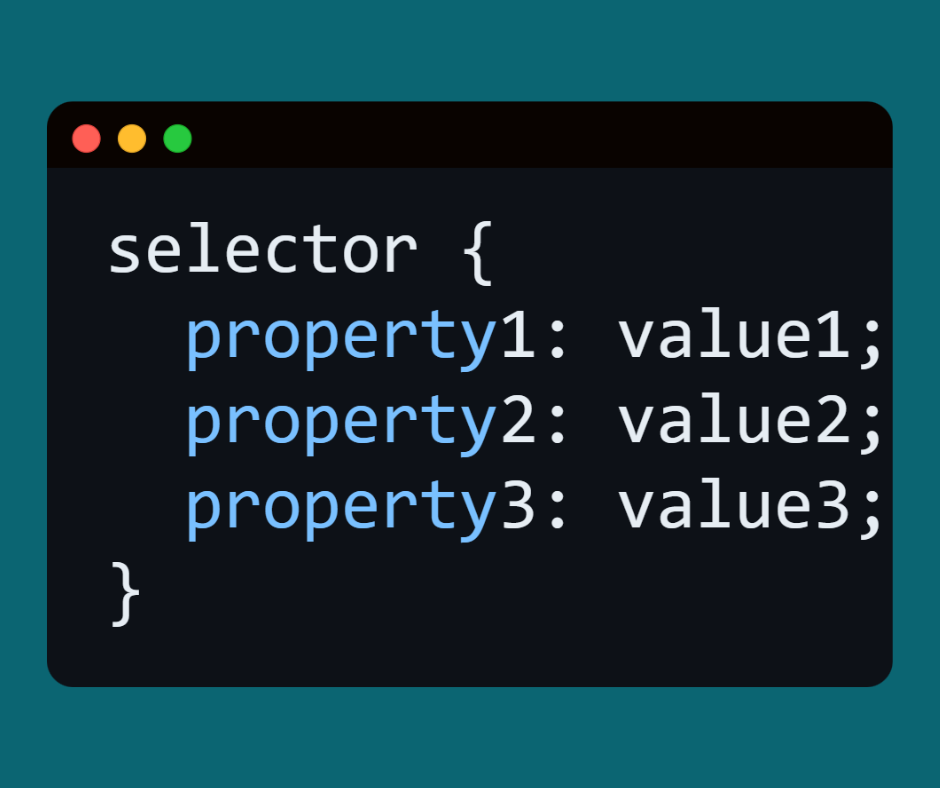
Any code in CSS has a specific structure:
Explanation of parts:
-
Selector → is what determines the element in the HTML page to which you want to apply the formatting.
-
Property → The type of formatting you want to do (e.g., color, font-size, margin).
-
Value → The value that determines the appearance of the property (e.g., red, 20px, center).
-
Each property ends with ; (semicolon).
🔹 Practical example:
-
p = selector (applies to all paragraphs).
-
color = property (will change the text color).
-
red = color value.
-
font-size = font size property.
-
18px = value.
4. Selectors
Selectors are the way you tell CSS: “Apply styling to any element with this condition.”
1️⃣ Element Selector
-
Selects all items of a certain type.
⬅️ Here is all <p> On the page it will be blue.
2️⃣ ID Selector
-
Selects the element with a specific id.
-
We use # before the id name.
⬅️ The formatting will only apply to this paragraph.
3️⃣ Class Selector
-
Selects elements that have a specific class.
-
We use . before the class name.
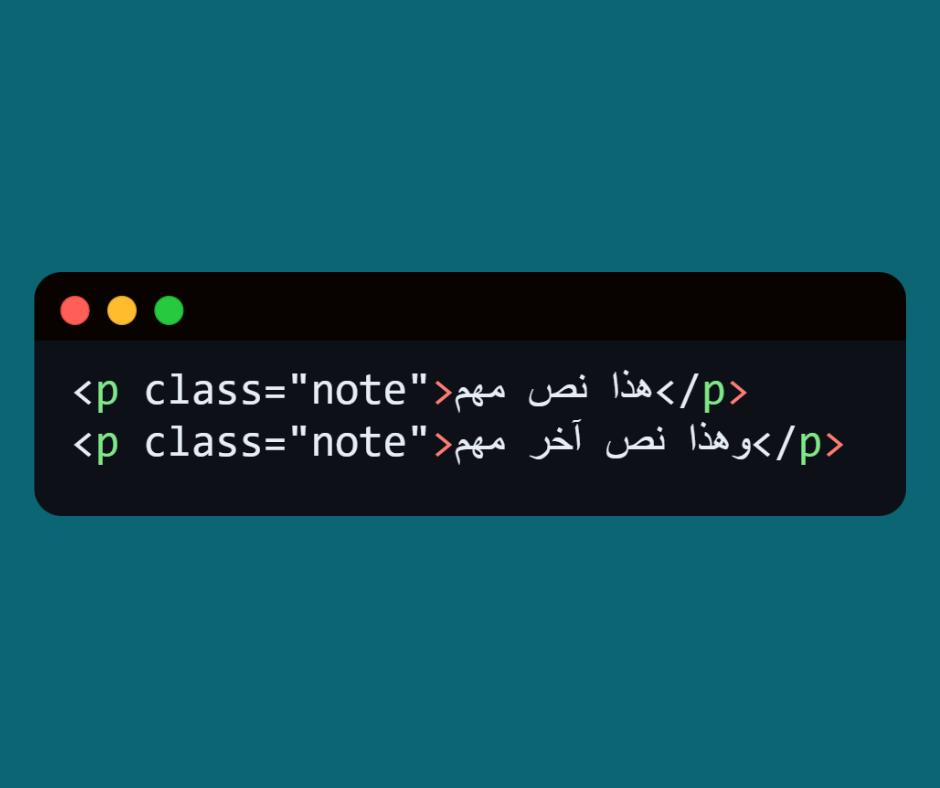
⬅️ The formatting will be applied to all elements that have class=”note”.
4️⃣ Universal Selector
-
Selects all elements on the page.
-
We use it when we want to apply a general rule.
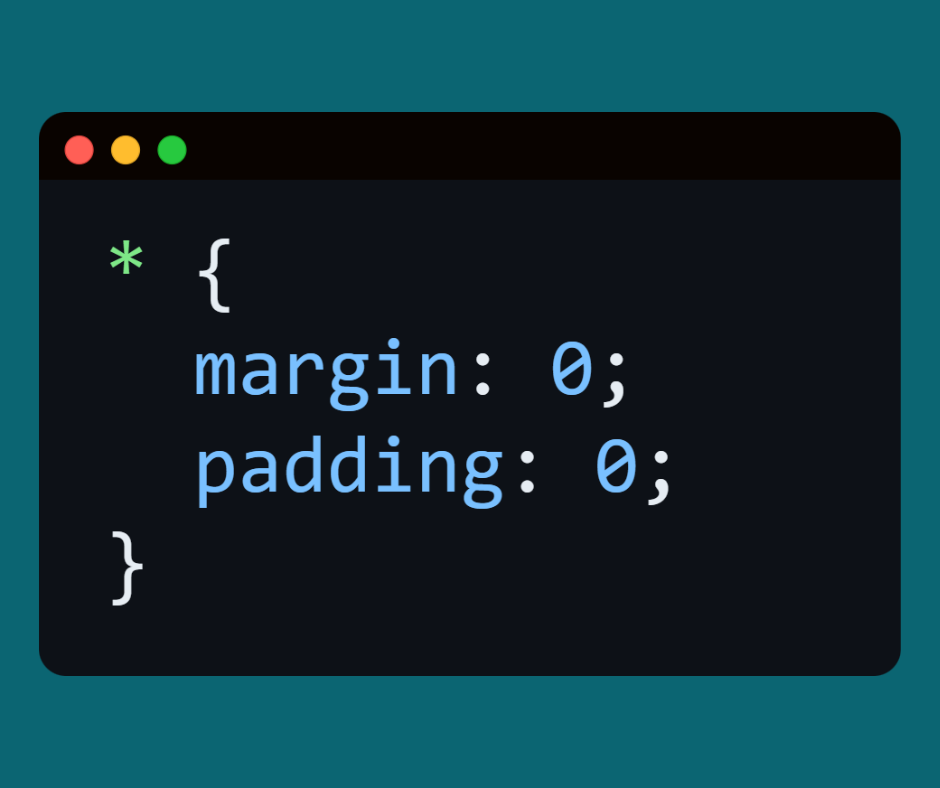
⬅️ Here we will remove the default spaces from all elements.
5️⃣ Group Selector
-
Allows us to select more than one item at a time.
-
We separate them with .
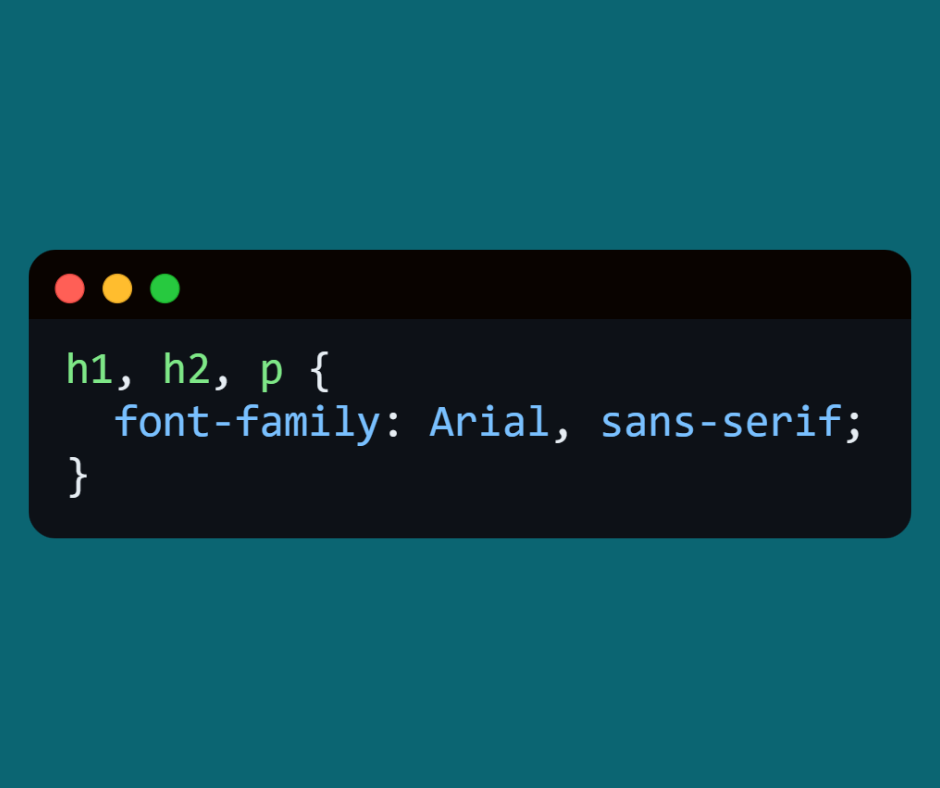
⬅️ Here the same font will be applied to all headings and paragraphs.
6️⃣ Descendant Selector
-
Selects the nested elements.
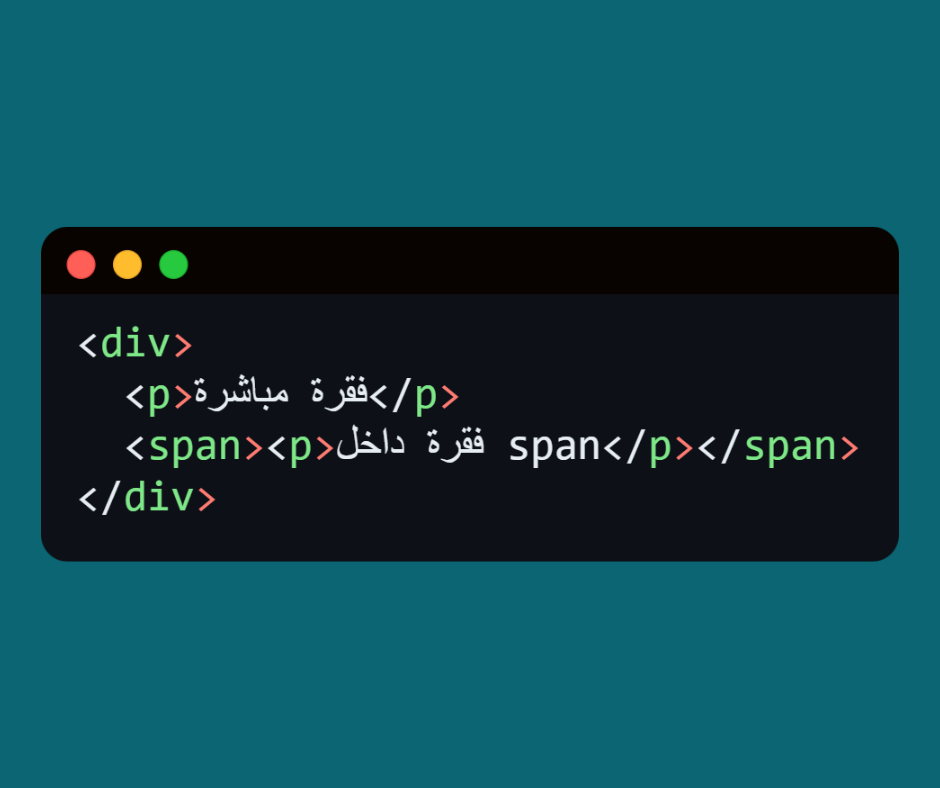
⬅️ It will change the color of the paragraph inside <div> only.
7️⃣ Child Selector
-
Selects elements that are direct children of a given element.
-
We use > between elements.
⬅️ It will only be applied to the paragraph directly inside the div.
8️⃣ Sibling Selectors
-
Adjacent Sibling (+) → Selects the element that comes immediately after a specified element.
-
General Sibling (~) → Selects all elements that come after a specified element at the same level.
📝 Quick summary
-
Element Selector → Selects a specific element (p, h1).
-
ID Selector (#id) → Applies to a single distinct element.
-
Class Selector (.class) → Applies to more than one element.
-
Universal (*) → applies to all.
-
Group(,) → Applies to a set of elements.
-
Descendant(div p) → Elements inside another element.
-
Child (div > p) → direct children.
-
Siblings (+, ~) → elements next to each other.
🟦 Level 1: CSS Basics
5. Properties & Values
🔹 What are the properties?
-
Properties are the “commands” we use in CSS to change the appearance of elements.
-
Each property has a value that determines its appearance.
-
example:
-
here:
-
color = property.
-
red = value.
-
🔹 Code composition with properties and values
📌 Example:
h1 → The element to be affected.
-
color: blue; → The color property and its value are blue.
-
font-size: 30px; → Font size property with a value of 30 pixels.
-
text-align: center; → The alignment property and its value are centered.
Common Properties with Values
🖌️ 1- Text Properties
-
color → Text color.
-
example:
-
color: red; or color: #ff0000;.
-
-
font-size → Font size.
-
Example: font-size: 20px;.
-
-
font-family → Font type.
-
Example: font-family: Arial, sans-serif;.
-
-
font-weight → line thickness.
-
Example: font-weight: bold; or font-weight: 400;.
-
-
text-align → Text alignment.
-
Example: text-align: center; or left or right.
-
-
text-decoration → Underline or underline the text.
-
Example: text-decoration: underline;.
-
-
line-height → the distance between lines.
-
Example: line-height: 1.5;.
-
🎨 2- Background Properties
-
background-color → Background color.
-
Example: background-color: yellow;.
-
-
background-image → Image as background.
-
Example: background-image: url('bg.jpg');.
-
-
background-repeat → Repeat image.
-
Example: background-repeat: no-repeat;.
-
-
background-size → Image size.
-
Example: background-size: cover;.
-
📦 3- Box Model Properties
-
width → Width of the item.
-
height → Height of the element.
-
margin → outer space around the element.
-
padding → Inner space between text and element borders.
-
border → element border.
-
Example: border: 2px solid black;.
-
-
border-radius → rounded corners.
-
Example: border-radius: 10px;.
-
✨ 4- Effects properties
-
box-shadow → shadow for the box.
-
Example: box-shadow: 0px 4px 8px gray;.
-
-
opacity → transparency of the element.
-
Example: opacity: 0.5; (semi-transparent).
-
✅ Important notes:
-
Every property must be followed by a value.
-
If you type an invalid value, the browser will ignore the line.
-
We can write more than one property for the same element inside { }.
-
Values can be:
-
Numbers + units (px, em, %, vh, vw).
-
Keywords (red, bold, center).
-
Color codes (#000000, rgb(0,0,0)).
-
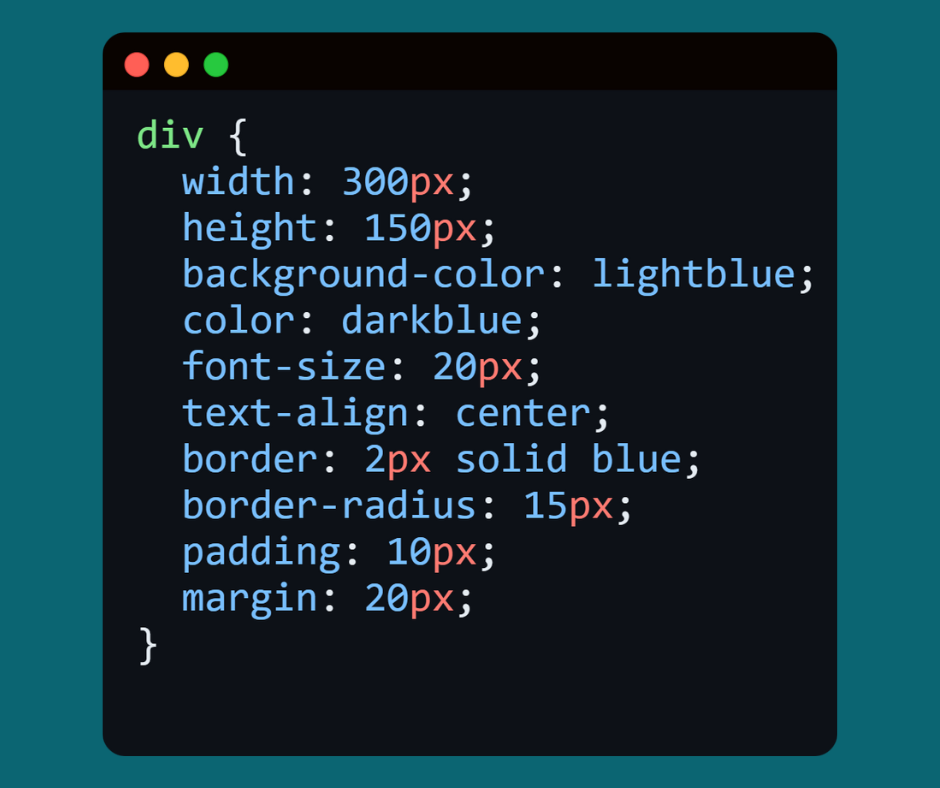
📌 An applied example that combines different properties:
-
A box 300px wide and 150px high.
-
Its background is light blue, and its texts are dark blue.
-
Texts are centered and 20px in size.
-
It has blue borders with rounded corners.
-
padding inner 10px, margin outer 20px.